Publications
2026
-
 TRASE: Tracking-free 4D Segmentation and EditingYun-Jin Li, Mariia Gladkova , Yan Xia , and Daniel Cremers2026 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 2026
TRASE: Tracking-free 4D Segmentation and EditingYun-Jin Li, Mariia Gladkova , Yan Xia , and Daniel Cremers2026 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 2026Understanding dynamic 3D scenes is crucial for extended reality (XR) and autonomous driving. Incorporating semantic information into 3D reconstruction enables holistic scene representations, unlocking immersive and interactive applications. To this end, we introduce TRASE, a novel tracking-free 4D segmentation method for dynamic scene understanding. TRASE learns a 4D segmentation feature field in a weakly-supervised manner, leveraging a soft-mined contrastive learning objective guided by SAM masks. The resulting feature space is semantically coherent and well-separated, and final object-level segmentation is obtained via unsupervised clustering. This enables fast editing, such as object removal, composition, and style transfer, by directly manipulating the scene’s Gaussians. We evaluate TRASE on five dynamic benchmarks, demonstrating state-of-the-art segmentation performance from unseen viewpoints and its effectiveness across various interactive editing tasks.
2025
-
 VXP: Voxel-Cross-Pixel Large-scale Image-LiDAR Place RecognitionYun-Jin Li, Mariia Gladkova , Yan Xia , Rui Wang , and Daniel Cremers2025 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 2025
VXP: Voxel-Cross-Pixel Large-scale Image-LiDAR Place RecognitionYun-Jin Li, Mariia Gladkova , Yan Xia , Rui Wang , and Daniel Cremers2025 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 2025Recent works on the global place recognition treat the task as a retrieval problem, where an off-the-shelf global descriptor is commonly designed in image-based and LiDAR-based modalities. However, it is non-trivial to perform accurate image-LiDAR global place recognition since extracting consistent and robust global descriptors from different domains (2D images and 3D point clouds) is challenging. To address this issue, we propose a novel Voxel-Cross-Pixel (VXP) approach, which establishes voxel and pixel correspondences in a self-supervised manner and brings them into a shared feature space. Specifically, VXP is trained in a two-stage manner that first explicitly exploits local feature correspondences and enforces similarity of global descriptors. Extensive experiments on the three benchmarks (Oxford RobotCar, ViViD++ and KITTI) demonstrate our method surpasses the state-of-the-art cross-modal retrieval by a large margin. The code will be publicly available.
2024
-
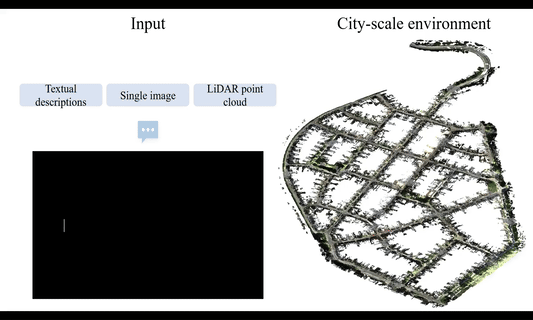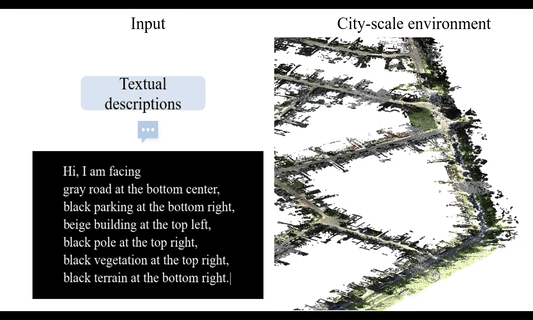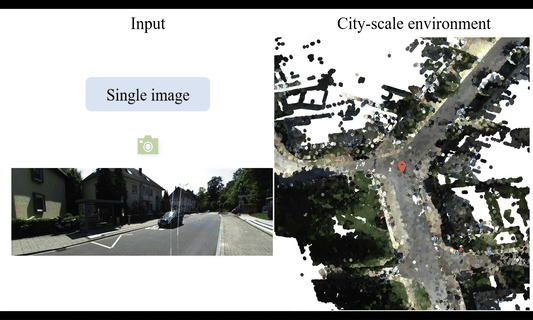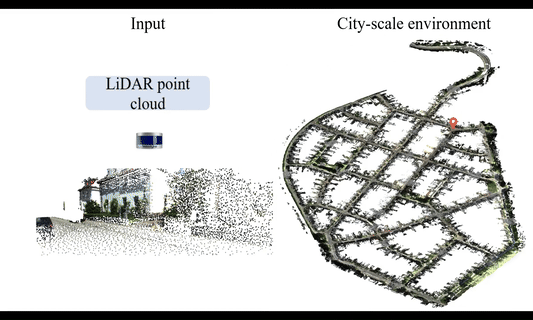 UniLoc: Towards Universal Place Recognition Using Any Single ModalityYan Xia , Zhendong Li , Yun-Jin Li, Letian Shi , Hu Cao , João F. Henriques , and Daniel CremersarXiv preprint arXiv:2412.12079, 2024
UniLoc: Towards Universal Place Recognition Using Any Single ModalityYan Xia , Zhendong Li , Yun-Jin Li, Letian Shi , Hu Cao , João F. Henriques , and Daniel CremersarXiv preprint arXiv:2412.12079, 2024To date, most place recognition methods focus on single-modality retrieval. While they perform well in specific environments, cross-modal methods offer greater flexibility by allowing seamless switching between map and query sources. It also promises to reduce computation requirements by having a unified model, and achieving greater sample efficiency by sharing parameters. In this work, we develop a universal solution to place recognition, UniLoc, that works with any single query modality (natural language, image, or point cloud). UniLoc leverages recent advances in large-scale contrastive learning, and learns by matching hierarchically at two levels: instance-level matching and scene-level matching. Specifically, we propose a novel Self-Attention based Pooling (SAP) module to evaluate the importance of instance descriptors when aggregated into a place-level descriptor. Experiments on the KITTI-360 dataset demonstrate the benefits of cross-modality for place recognition, achieving superior performance in cross-modal settings and competitive results also for uni-modal scenarios. The code will be available upon acceptance.

